What They Are, How to Spot Them, and How to Stay Safe
The internet is a space filled with opportunities, but it’s also home to hidden dangers. One of the most prevalent threats online is phishing—a sneaky tactic cybercriminals use to steal your personal information. Phishing scams can be so convincing that even the most cautious among us might fall for them. But what exactly is phishing, why is it a widespread problem, and most importantly, how can you protect yourself? This article will explore phishing in detail, breaking it down into simple, easy-to-understand language so that everyone—from tech novices to seasoned professionals—can learn to stay safe online.
What Is Phishing?
Phishing is a type of cyberattack where criminals try to trick individuals into giving away sensitive information such as passwords, credit card numbers, or other personal data. These scams are typically carried out using emails, text messages, or fake websites that look surprisingly legitimate. The goal? To make you believe you’re dealing with a trusted organization, like your bank, a government agency, or even your email provider, so you willingly hand over information.
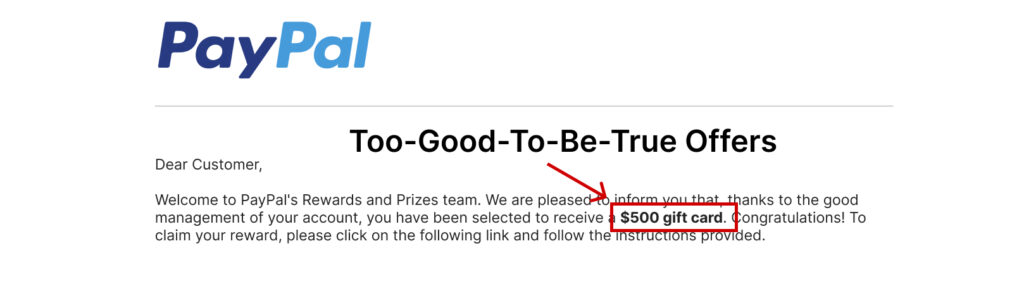
The term “phishing” is considered a play on the word “fishing” because attackers cast out bait (fake messages) hoping victims will “bite” by clicking on links or providing sensitive data. Whether it’s an email claiming you’ve won a lottery or a message warning your account will be suspended unless you act fast, the tactic always revolves around evoking urgency and emotional responses like fear or excitement.

Why Do Cybercriminals Do It?
Phishing isn’t just a random act of trickery—it’s highly calculated. Cybercriminals engage in phishing for various reasons:
Phishing often aims to access bank accounts or credit card details for immediate financial gain.
Personal information obtained through phishing can be used to impersonate you, open fraudulent accounts, or commit other forms of fraud.
Businesses are also frequent phishing targets, with criminals looking to gain sensitive company data, which could include trade secrets or customer information.
Some phishing attacks trick users into downloading malicious software (malware), which can steal information or harm devices.
The end goal is always some form of financial or informational gain for the attacker—often at your expense.

How to Spot a Phishing Attempt
Phishing scams can be sophisticated, making them harder to identify. However, many phishing attempts share common characteristics. Here are clear signals to look out for:
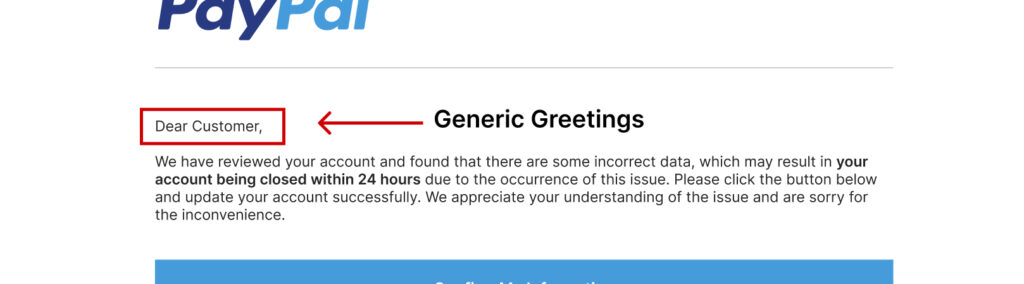
1. Generic Greetings
Phishing emails often address you with phrases like “Dear Customer” or “Dear User” instead of your name. This is because the sender doesn’t know who you are—they’re targeting thousands of people simultaneously.
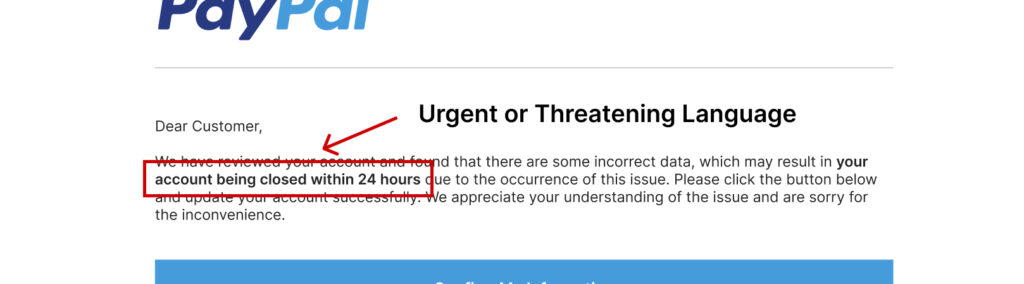
2. Urgent or Threatening Language
Messages that create a sense of urgency, like “Your account will be deactivated TODAY unless you update your information,” are often phishing attempts. Cybercriminals play on fear and panic to pressure you into acting quickly.
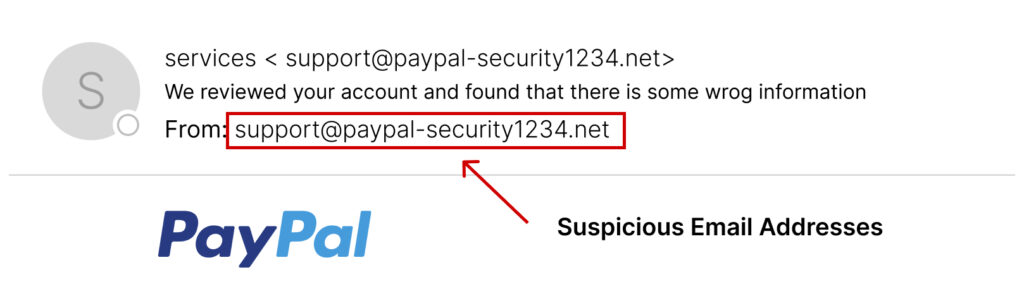
3. Suspicious Email Addresses
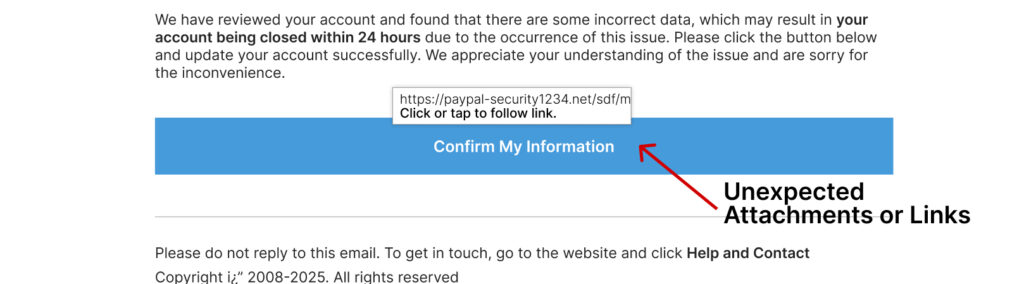
Always glance at the sender’s email address. For example, an email from PayPal should come from an address ending in @paypal.com. If it’s something like @paypal-security1234.net, it’s a red flag.
4. Unexpected Attachments or Links
If an email contains an attachment or a link you weren’t expecting, proceed with caution. Clicking these can trigger malware downloads or lead to fake websites designed to steal your information.
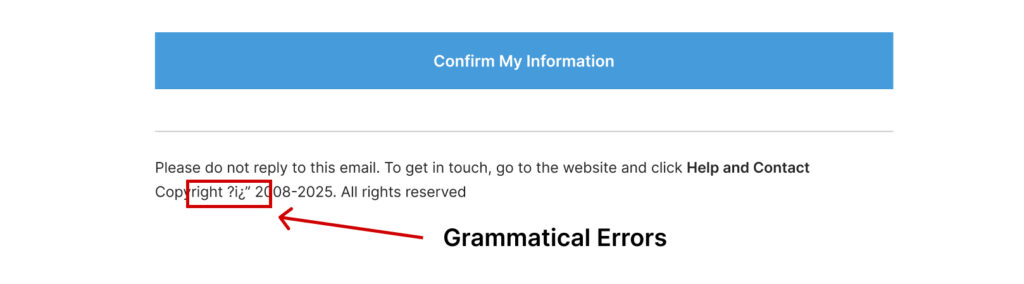
5. Grammatical Errors
Poor spelling, unusual language, and inconsistent formatting are common in phishing emails. While advanced attackers are improving on this front, many phishing attempts still have these telltale signs.
How to Differentiate Phishing from a Legitimate Request
Distinguishing between phishing scams and genuine communications can be challenging. Here’s a breakdown to help:
Scenario 1: The “Hosting Cancellation” Scam
Imagine receiving the following email:
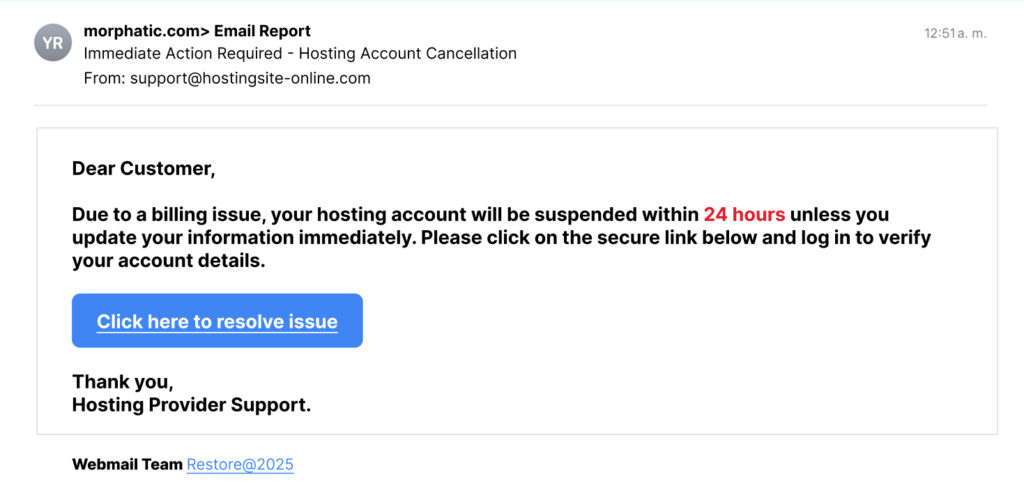
At first glance, this email might seem real, especially if you use a hosting service. However, upon closer inspection, you’d notice discrepancies:
1. Check the email address: “support@hostingsite-online.com” might closely mimic the legitimate hosting provider, but there’s an extra hyphen or a slight typo. Genuine communications always come from official domains.
2. Hover over the link: Without clicking, hover your mouse over the link. If the URL looks odd or doesn’t match the official website, it’s probably a phishing attempt.
3. Contact your provider directly: Instead of clicking, call or email your hosting company using verified contact info.

Scenario 2: Tech Support Scams
You get a pop-up alert on your screen saying:
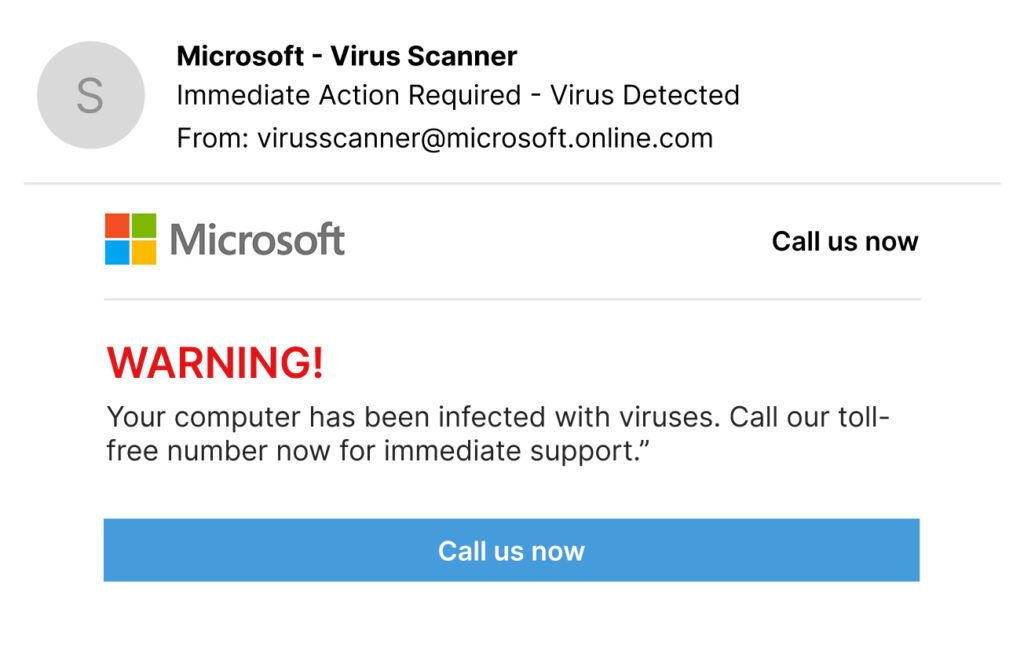
This is a classic phishing ploy. Legitimate companies like Microsoft or Apple will not send pop-ups asking you to call them. If something feels off, it probably is.

Scenario 3: The Fake Payment Request
An email arrives claiming:
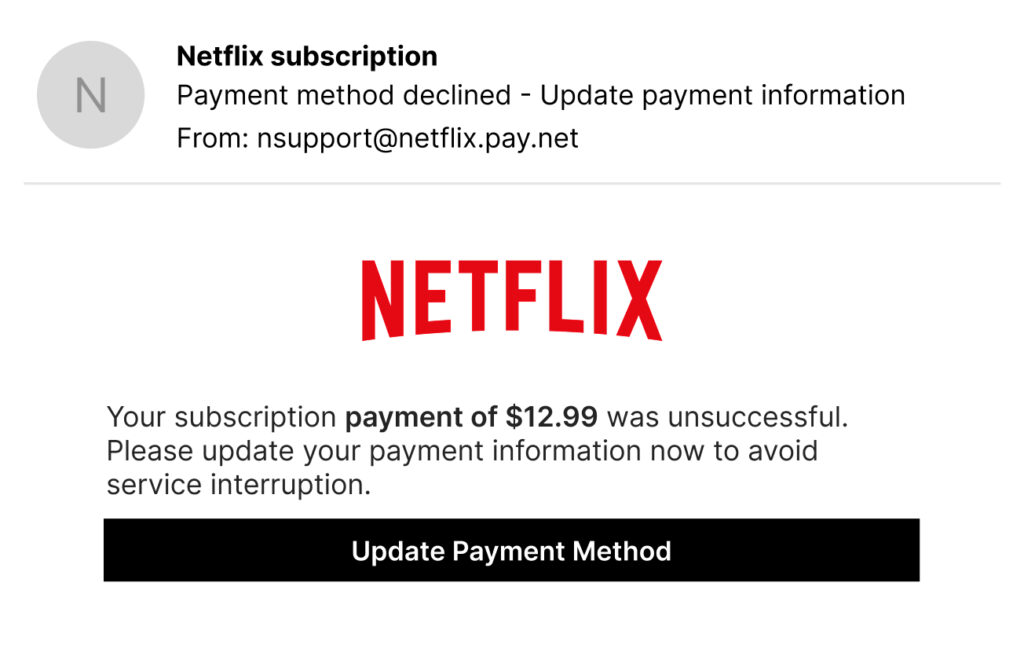
A legitimate company would always offer alternative ways to verify billing issues outside of email, such as app notifications or direct account logins. Never submit payment details via email. Log in to your account through a trusted browser instead.

What Not to Do When You Encounter Phishing
When you come across a suspicious email or message, remember these don’ts:
1. Don’t Click on Links – Clicking could lead you to malicious websites.
2. Don’t Provide Personal Information – Avoid sharing anything like passwords, PINs, or credit card details.
3. Don’t Download Attachments – File downloads could contain viruses or ransomware.
4. Don’t Call Suspicious Numbers – Scammers often set up fake helplines to trick you into giving away details over the phone.

How to Stay Safe Online
Use Email Filters
Most email providers, like Gmail, offer robust spam filters that can block many phishing emails from reaching your inbox.
Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
Even if someone steals your password, two-factor authentication adds an extra layer of security. This way, they can’t access your account without your second verification method (e.g., a one-time code sent to your phone).
Install Reliable Security Software
Anti-malware and antivirus programs can detect and block phishing threats before they harm you.
Stay Educated
A little knowledge can go a long way. Regularly update yourself on the latest phishing trends so you know what to watch for.
Verify Contacts Before Sharing Information
If you receive a request for sensitive information, always verify its authenticity by contacting the organization directly via official channels.
Update Your Passwords Regularly
Strong and unique passwords for every account can minimize damage if one of your accounts is compromised.

Final Thoughts
Phishing attacks are constantly evolving, but so are the tools and knowledge that help prevent them. By understanding what phishing is, recognizing warning signs, and implementing online safety best practices, you can shield yourself from becoming a victim. Remember, staying vigilant and informed is your best defense against cybercrime.